Curiositas Fall 2021:
Curiositas Fall 2021 was digitally published December 6th, 2021.

Writing Center Research: Reflecting on "Radical Reciprocity in Online Spaces"
Link to Read "Reflecing on Radical Reciprocity" (PDF)
Writing Center peer tutor, Abby Bernard, describes her journey with Writing Center research. Bernard frst explains her understanding of Michele Eodice’s concept of “participatory hospitality” before examining participatory hospitality in online, asynchronous writing studios. This inquiry presents an opportunity to further understand which tutoring practices may foster participatory hospitality, as well as demonstrates the process of research within Writing Center scholarship.
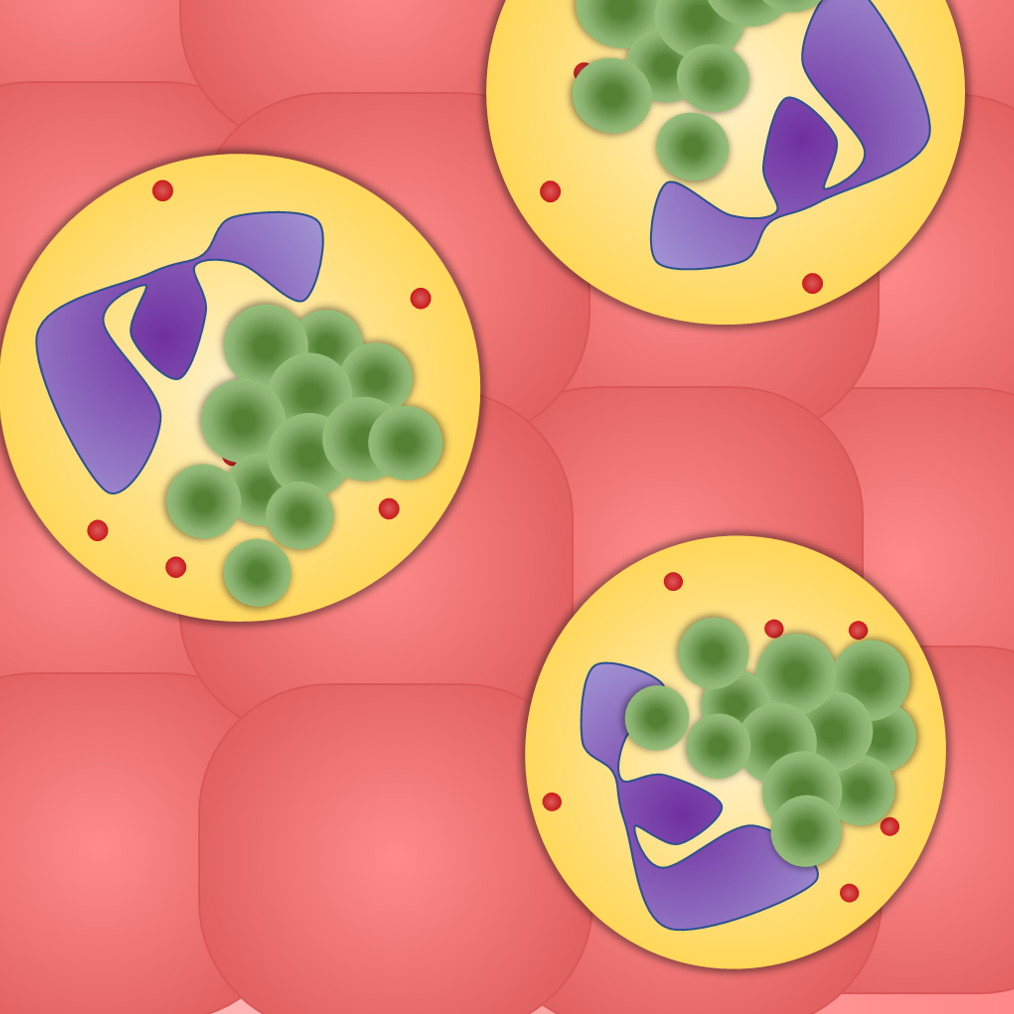
The SaeR/S Two Component System: The Security System of Staphylococcus aureus
Link to Read "The SaeR/S Two-Component System" (PDF)
Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) is a common human pathogen that is responsible for thousands of deaths each year. The bacterium’s severity is caused, in part, by its ability to detect and evade the human immune system. In this article, Owen Burroughs, an undergraduate researcher in the lab of Dr. Jovanka Voyich, describes his research into the SaeR/S two-component system, a “security system” that allows S. aureus to avoid being killed by immune cells. Over the course of Owen’s research, the Voyich lab has determined that the proteins SaeP and SaeQ likely play a major role in the functioning of this security system. By helping us better understand the interactions between S. aureus and its host, this research could pave the way for new treatments and therapies for severe S. aureus infection.

Purple Dreamscape and Soft Green Haze
Link to Read "Soft Green Haze and Purple Dreamscape" (PDF)
“Soft Green Haze” and “Purple Dreamscape” are two oil paintings on wood panels by Olivia Ross, a Studio Art student at Montana State University. In creating these two works, Olivia looks to examine how narrative and aesthetic choices draw a viewer into a piece. Olivia removed any indication of a clear narrative or recognizable spaces and instead relies on abstraction to prompt an audience to engage. Olivia found even with the absence of these the viewer is enticed to explore further, not only in physical proximity to the work, but in projecting their own ideas onto it. Olivia thinks that this inclination to create one’s own relationship with a piece when there is no clear narrative to grasp makes a nontangible, abstracted space that’s much more reactively powerful.
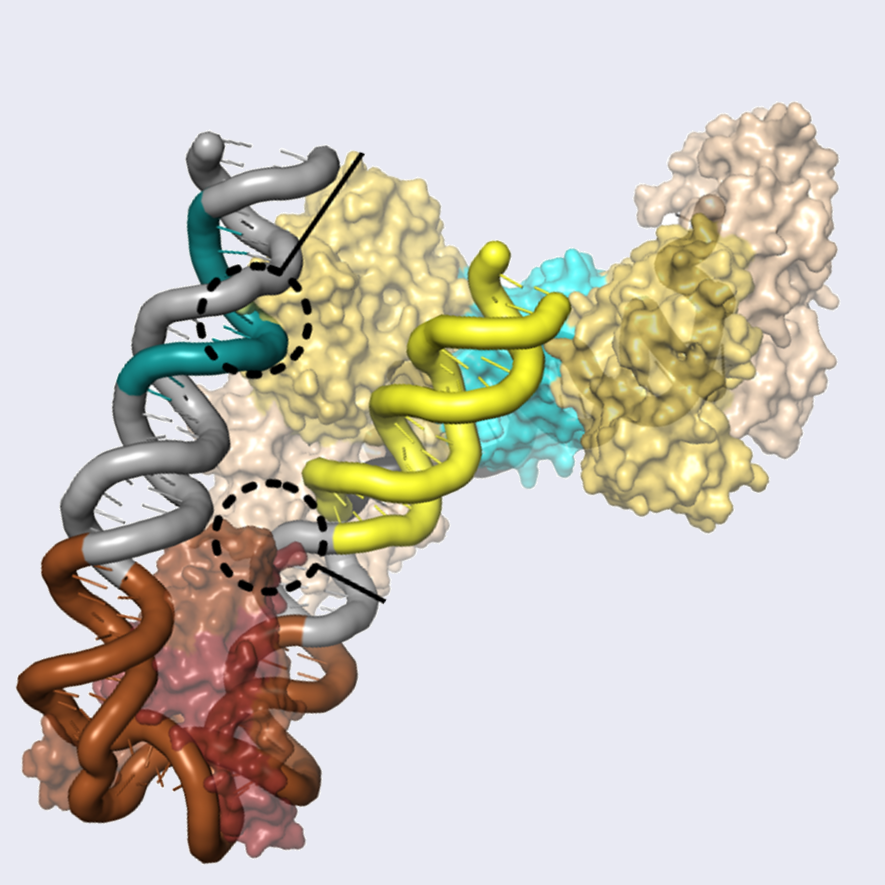
Bioinformatic Identifcation of CRISPR Leader Motifs
Link to Read "Bioinformatic Identification of CRISPR Leader Motifs" (PDF)
Clustered Regularly Interspersed Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR) and CRISPR associated (Cas) proteins serve as a sophisticated adaptive immune system to defend bacteria and archaea from viral infection. CRISPR mediated immunity occurs in three stages which allow the bacteria to adapt and respond to new as well as previously encountered viruses. The initial step of CRISPR adaptation requires the help of the Integration Host Factor (IHF) and a stretch of 200 base pairs known as the CRISPR leader to ensure encounters with new viruses are properly recorded in the host organism’s immunological memory. A bioinformatic analysis of over 15,000 CRISPR leaders reveals that IHF is a prevalent and widespread feature of CRISPR adaptation across several diferent CRISPR subtypes and host organisms.
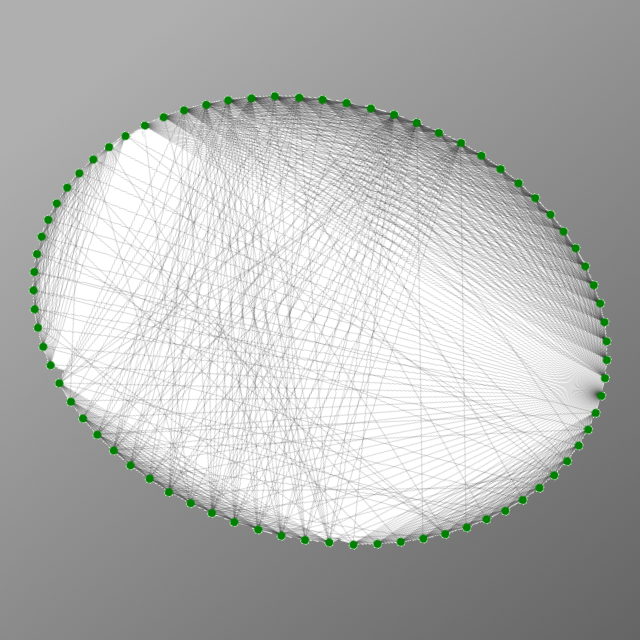
Approximating Expensive Distance Metrics
Link to Read "Approximating Expensive Distance Metrics" (PDF)
Computing the distance between point a and point b is typically considered to be very easy. However, there are times when computing a distance can take signifcant computation time; we call these expensive distance metrics. Suppose we have some expensive distance metric and we need to compute the distances between a bunch of points. This paper explores a method that to reduce the number of queries to the distance metric and the efect on clustering. The authors fnd that total run time can be reduced while only inducing small inaccuracies in clustering output.
