Ergonomics Program
Ergonomics is fitting the task to the worker. It is finding the best way to arrange workstations so the worker can perform his/her activities efficiently and safely. While ergonomics is important and commonly recognized as being applicable in the office environment, it is also important in non-office settings.
Are you experiencing pain? If you are an office worker (sitting at a workstation/computer for at least 2 hours a day) and you are experiencing pain/discomfort or recognize that your chair/computer/keyboard/etc. is not set up appropriately, please visit our Office Ergonomics section. If you are an employee that works in a laboratory environment, please visit our Lab Ergonomics section. If you are an employee that does not work at at workstation consistently but are experiencing pain, discomfort, or perform repetitive tasks, please visit our Field Ergonomics section.
Office Ergonomics
There are a significant number of changes you can make on your own to alleviate or prevent pain/discomfort without the help of an ergonomic specialist, as well as what is on the Self-Assessment Check Sheet. The flow chart to the right is an outline of the process to assist in the corrections to alleviate pain/discomfort. Click on any of the boxes with yellow outlines to access the item described.
Here are some additional images and descriptions to help you make adjustments to your
workstation on your own.
Chair Adjustment and Posture
Your Chair should be adjusted to fit you, and this is the most important piece of equipment you can purchase and adjust appropriately. Below are some correct and incorrect ways to sit and stand at your workstation.
Correct


Incorrect

Correct posture and using the chair to appropriately support your back will help alleviate pain in your shoulders, lower and upper back. The image on the right is commonly seen with office employees where they are hunched over, looking down at a monitor. They also typically are not using the back of the chair to support their back, creating more stress on the inappropriate curvatures of their back. The two images on the left show the individual with a tall posture, and his gaze straight ahead.
Incorrect

Correct

Foot trays may be used when a desk is high enough that adjusting your chair to the appropriate height pulls your feet off the ground. Notice in the image on the right that his feet are pointed versus being at a 90° angle. Additionally, in the image on the right, his knees are pushed up which creates more pressure on the parts of his legs that are touching the chair.
Monitor Adjustment
Your monitor(s) should be adjusted properly to reduce the strain on your neck and eyes. We will look at how to adjust monitors in ways that were not covered in the training video. This includes dual displays and rotating displays.
Split

The left image, as seen above, is to split the screens evenly, so the seam of the two is directly in front of you. This is applicable for folks that constantly use both monitors simultaneously, and neither more predominately.
Offset

The right image, as seen above, is to have one primary monitor directly in front of you, and one off-set. This is applicable for folks that consistently use one predominant monitor, and the other is for reference or rarely used.
Adjusting 1 Monitor Vertically

For some individuals, it may be applicable to have one monitor rotated 90°. If you are interested in how to make your computer image rotate on the screen, various instructions may be found on the internet - here is one example. This is a handy option for folks that often look at long excel files or long documents.
Laptop Adjustments
This section applies to folks that use a laptop, whether temporarily or permanently, without external monitors.
Correct

Incorrect

The only difference between the two images above is the worker is resting his wrists on the desktop on the image on the right. This is a common cause and irritator of Carpel Tunnel Syndrome.
Correct

Incorrect

The worker's chair is too low causing an upward angle in his arms to reach the keyboard.

The worker has poor posture due to having to look down. This often causes back pain as well as lower body nervous issues.

With the laptop even lower, on his lap, he has to have a much more downward facing gaze, which causes significant strain on his neck.

While this position looks comfortable and how we would love to 'kick back' to work, it is hard and stressful on our shoulders, neck, and back.
Tablets - Desktop Use
This section applies to folks that use a tablet, whether temporarily or permanently. As these become more commonplace in our workplace, additional injuries will arise from improper use. The best use is to not use one for any significant period of time.
Correct

If at all possible, place the tablet at eye height and use an external keyboard.

Stack up books/paper or whatever is available to give more height and use an external keyboard.
Incorrect

Stacking items under the tablet will help to bring it up to a level where less strain occurs on the back/neck.

If at all possible, use an external keyboard if typing more than a quick reply. Notice the amount of unnatural curvature in this worker's back due to the low screen.
Phone - Desktop Use
This section applies to folks that use a Phone with regularity in their office.
Correct

Using handsets is simple and convenient for infrequent users.
Using a headset is vitally important for individuals that perform computer research while on the phone, or for users that constantly answer the phone.
Incorrect

Pinching the phone between the ear/shoulder causes strain on the neck, and supporting muscles of the head and back. Individuals that find themselves using this method should look into a headset.
Computer Mice
This section applies to folks that use peripheral mouse for their computer, whether laptop or desktop.
Correct

This mouse is the appropriate size for the individual. His fingers do not hang off the front of the mouse and it fits well in his palm.
Incorrect


These mice are too small for the individual. His fingers hang off the front, or require excessive bending to touch the buttons. They do not fit in his palm at all.
Correct

This is the correct use of a wrist support, if one will be used.
Incorrect
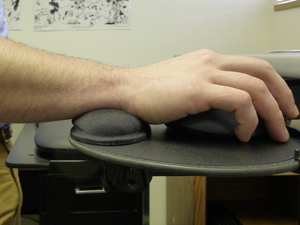
This is an incorrect use of a wrist support, if one will be used.
Chair Vendors
Below is a list of local office furniture supply vendors that offer chair trial periods varying from a few days to a week or more to ensure the right fit before you buy. They will swap out trial/demo chair models as many times as you need. New chair factors to take into account when purchasing: arm rest adjustability, seat back adjustability, seat pan adjustability, and padding rated for 8 or more hours of sitting. We highly recommend not purchasing chairs from a Big Box/Chain Office Supply Store.
Bring chairs to you:
Go to their showrooms:
Lab Ergonomics
Personnel that work in laboratory environment often perform numerous repetitive motions throughout the day, as well as sit in stools leaning over a bench, or peering into microscopes for long periods of time. There are several actions you can take to help reduce your changes of incurring an ergonomic related injury on the job.
All employees working at a computer or adjusting chairs should revisit the Office section above for adjusting chairs/monitors. Prior to requesting an ergonomic evaluation, please use the flowchart listed in the above section.
Field Ergonomics
Personnel that work outdoors, or performing activities that fall outside of laboratories and sitting in front of a computer should contact an SRM Ergonomic Specialist to review your situation. Please submit a request for an ergonomic assessment to be completed.
