Research Areas
Research Focus Areas of the MSU Breeding Program |
|
Management |
Quality |
Improvement |
Genetic Disection |
Why research barley at MSU?
-
Production has moved west
- U.S. barley acres in the Midwest have been declining due to competition from other crops such as corn and soy beans as well as high risk of fungal disease (specifically Fusarium Head Blight, FHB or "Scab")
-
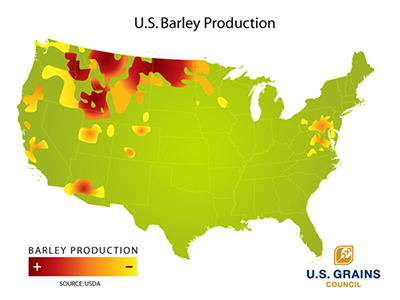
Montanan's plant more barley acres than any state
-
Other large producers are also within our region including Idaho and the Dakotas
-
-
Barley is an important part of crop rotation to manage pests
-
such as wheat stem sawfly and cheat grass
-
-
Barley has many end-uses providing multiple markets for growers
- Malt barley has the highest economic return
Grower Issues
- 80% of Montana farmland is rainfed
- Barley grown on rainfed is more likely to be rejected for malt
- Revenue lost when rejected for malt due to poor quality
- Primary reason for rejection:
- High protein
- Poor plumps
MSU Barley Crossing Block by Year:
| Breeding Goals | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 |
| Spring Breeding | |||||||
| High yield, high quality malt or feed | 90 | 87 | 29 | 39 | 19 | 23 | 36 |
|
Heirloom malt |
75 | 90 | 94 | 76 | 25 | ||
| Food | 19 | 21 | 23 | 16 | 35 | ||
| Forage | 12 | 12 | 11 | 14 | 5 | 56 | 50 |
| Purple malt for food | 15 | 23 | 6 | 8 | 20 | ||
| Digestibility | 4 | ||||||
| Lodging resistance | 11 | 1 | |||||
| FHB resistance | 14 | 22 | 13 | 12 | 8 | 23 | 21 |
| Extended grain-fill (high yield, stable quality) | 31 | 12 | 7 | ||||
| Spot Form of Net Blotch Resistance | 3 | 12 | 14 | ||||
| Nematode resistance | 4 | 10 | 1 | ||||
| Stem Rust | 11 | ||||||
| Stripe Rust | 2 | 4 | 12 | 10 | |||
| Beer staling resistance | 6 | ||||||
| Bacterial Leaf Streak Resistance | 10 | ||||||
| Acid Tolerance | 20 | 11 | 4 | ||||
| Low proline | 6 | ||||||
| Low GN | 2 | ||||||
| Winter Breeding | |||||||
| Forage | 8 | 39 | 24 | ||||
| Cold Tolerance | 21 | 57 | 17 | ||||
| Malt / feed | 45 | 53 | 57 | ||||
| Food | 1 | ||||||
| Hull-less | 3 | 2 | |||||
| Low B-glucan | 4 | ||||||
| Low GN | 2 | ||||||
| Stay Green | 4 | ||||||
| Fast hydrating/dormant | 8 | ||||||
| Low proline | 1 | ||||||
| Stripe Rust | 3 | ||||||
Breeding Program - Flow from 1st cross to variety release
Core nurseries conducted each year for the barley breeding program. For locations other than Bozeman, the work is accomplished by the Research Center faculty and staff.
| Nursery | Number of Lines | Location | Notes |
| Crossing Block | Intercrossing of about 100 parents | Bozeman - Plant Growth Center | Parents include superior varieties from MSU and other regional programs as well as diverse germplasm from around the world. |
| F1 | 150 | Bozeman - Plant Growth Center | First generation following crossing |
| F2 and F3 | 12000 | Bozeman - Plant Growth Center | Inbred lines are developed without selection via single seed decent |
| F4 | 12000 | Bozeman - Post Farm | Individual plants selected for height, grain protein, kernel hardness and plant type. |
| F5 | 2500 | Bozeman - Post Farm | Rows selected for agronomic appearance, hardness, grain protein, and select quality traits |
| F6 - Preliminary Yield Trial (PYT) | 400-600 | Bozeman - Post Farm | Replicated nurseries selected for yield and quality |
| F7 - Early Yield Trial (EYT) | 64 | Bozeman, Havre, Sidney, Moccasin | Replicated yield trials with full malt tests or other end-use quality tests |
| F8-F10 - Advanced Yield Trial | 49 | Bozeman, Havre, Sidney, Moccasin, Huntley, Creston, Conrad | Replicated yield trials with full malt or other end-use quality tests |
| Winter nursery | 100 | CARC and EARC | Full plots, winter survival and malt |
| Foundation Seed: Increase/Variety Purification | 2-4 elite lines | Bozeman - Post Farm | Pure seed grown for distribution the following year |
